Benzena dan Turunannya: Pengertian, Rumus, Soal
Pernahkah kamu mencium bau wangi kapur barus dari lemarimu?
Senyawa apa yang sebenarnya terkandung dalamnya sehingga dapat menghasilkan aroma yang khas tersebut?
Ya, senyawa tersebut mengandung hidrokarbon aromatik, yaitu senyawa turunan benzena. Begitu banyak senyawa turunan benzena kita temui sehari-hari.
Bagaimana struktur, tata nama, dan kegunaan benzena dan turunannya? Marilah kita pelajari lebih lanjut agar lebih jelas.
Daftar Isi
Pengertian Benzena
Benzena merupakan senyawa hidrokarbon aromatik paling sederhana dengan rumus molekul C6H6 yang berbentuk siklik (membentuk cincin).
Benzena memiliki satu atom H yang terikat di setiap atom C dan memiliki total 3 buah ikatan rangkap dua yang berselang-seling.
Terdapat dua jenis cara menggambar struktur benzena yaitu dengan struktur Kekule dan struktur delokalisasi π.
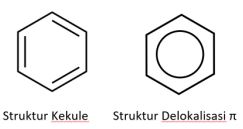
Struktur Kekule dikemukakan oleh Kekule pada tahun 1865.
Kekule menyatakan bahwa 6 atom karbon benzena berada pada sudut-sudut yang membentuk heksagon beraturan dengan satu atom hidrogen mengikat pada setiap atom karbon dengan ikatan tunggal dan ikatan ganda berseling.
Pada struktur delokalisasi π, ikatan rangkap pada benzena digambarkan sebagai lingkaran yang menyatakan terjadinya delokalisasi ikatan π.
Delokalisasi ini terjadi karena elektron pada ikatan rangkap yang berseling itu tersebar di seluruh cincin.
Mengapa kita perlu mempelajari benzena sedangkan strukturnya hanyalah sangat sederhana?
Meskipun benzena hanyalah cincin aromatik dengan enam atom karbon, pada kenyataan senyawa ini banyak kita temui sehari-hari.
Senyawa benzena memiliki berbagai turunan senyawa. Apa saja turunan senyawa benzena itu? Mari kita bahas lebih lanjut.
Senyawa Turunan Benzena dan Tata Namanya
Dari banyak turunan senyawa benzena yang ada, terdapat tiga jenis penggolongan senyawa benzena, yaitu benzena monosubstitusi, benzena disubstitusi, dan benzena substitusi lebih dari dua.
Benzena monosubstitusi merupakan benzena dengan satu substituen yang menggantikan salah satu atom H. Benzena jenis ini memiliki tata nama “nama substituen + benzena”. Perhatikan contoh berikut.
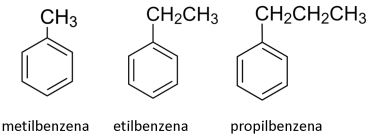
Nama-nama substituen yang umum terdapat pada senyawa benzena antara lain:
| Nama Substituen | Rumus/Struktur Kimia |
| nitro | -NO2 |
| floro | -F |
| kloro | -Cl |
| bromo | -Br |
| isopropil | -CH(CH3)2 |
| hidroksi | -OH |
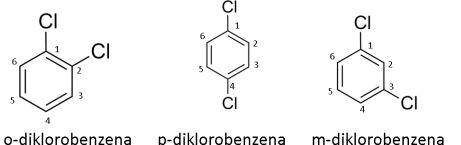
Benzena disubstitusi memiliki dua substituen sehingga dapat terjadi isomer posisi. Untuk membedakan isomer posisi pada benzena disubstusi, digunakan penamaan orto (o), meta (m), para (p).
Orto digunakan apabila substituen berada pada atom C nomor 1 dan 2. Meta digunakan apabila substituen berada pada atom C nomor 1 dan 3. Sedangkan para digunakan apabila substituen berada pada atom C nomor 1 dan 4.
Penomoran tentunya memperhatikan substituen terdekat sehingga tidak ada 1 dan 5 melainkan pada nomor 1 dan 3. Untuk lebih jelasnya perhatikan contoh berikut.
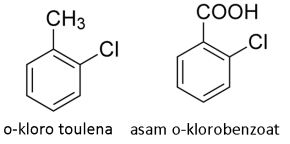
Bagaimana jika substituennya berbeda?
Apabila substituennya berbeda maka salah satu substituen menjadi senyawa utama sedangkan yang lain menjadi cabangnya.
Pemilhan senyawa utama memperhatikan aturan dibawah ini, dimana senyawa yang lebih diprioritaskan menjadi senyawa utama.
(lebih prioritas) –COOH, –SO3, –CH3, –CN, –OH, –NH2, –R, –NO2, –X
Nama-nama senyawa dengan substituen tersebut sebagai berikut.
| Benzena dengan substituen | Nama senyawa |
| –COOH | Asam benzoat |
| –COO– | Benzoat |
| –SO3– | Sulfonat |
| –SO3H | Asam Sulfonat |
| –CH3 | Toluena |
| –CN | Benzonitril |
| –OH | Fenol |
| –NH2 | Fenilamin |
| –NO2 | Nitrobenzene |
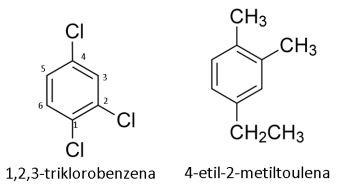
Nah, lalu bagaimana jika lebih dari dua substituen? Cara penamaannya hampir sama.
Untuk senyawa dengan substituen sama maka diberi nomor dengan substituen terdekat menjadi nomor 1, kemudian digunakan penamaan seperti pada senyawa organik umumnya.
Sedangkan pada substituen yang berbeda, salah satu substituen menjadi senyawa utama. Untuk lebih jelasnya, perhatikan contoh berikut ini.
Kegunaan Senyawa Benzena dan Turunannya pada Kehidupan Sehari-Hari
Tentunya kita sering sekali bertemu jenis senyawa ini, hanya saja kita sering tidak sadar dengan hal itu.
Apa saja sih kegunaan senyawa benzena ini dalam kehidupan kita? Senyawa seperti apa itu?
Berikut beberapa contoh senyawa benzena dan turunannya dalam kehidupan sehari-hari.
- Natrium benzoat, sebagai pengawet makanan
- Nitrobenzena, digunakan pada pewangi pada semir sepatu
- Asam salisilat, digunakan pada obat kutil, jerawat, dan ketombe
- Metil salisilat, digunakan pada balsam
- Asam benzoat, merupakan bahan baku untuk membuat sakarin, dan aspirin.
- Parasetamol, sebagai obat penurun panas
- Vanilin, sebagai perisa dan aroma vanila
Cukup banyak bukan?
Seperti biasa untuk memahami materi lebih lanjut, ayo kita kerjakan contoh soal.
Contoh Soal Benzena dan Turunannya
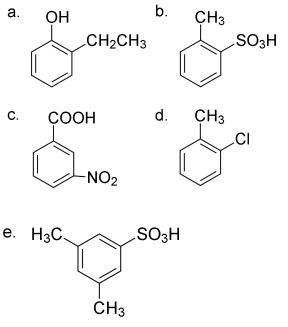
1. Benzena memiliki banyak turunan. Berikut beberapa contoh struktur turunan benzena. Beri nama masing-masing senyawa ini!
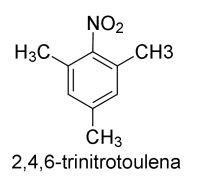
2. Salah satu jenis bahan peledak yaitu trinitrotoulena. Tuliskan struktur senyawa tersebut!
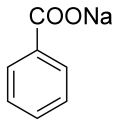
3. Natrium benzoat merupakan jenis pengawet turunan benzena, tuliskan struktur senyawanya!
1. nama masing-masing senyawa:
a. Etilfenol
b. Asam metilsulfonat
c. Nitrobenzoat
d. Klorotoulena
e. Asam 3,5-dimetilsulfonat
2. Struktur trinitrotoulena seperti berikut ini.
3. Struktur natrium benzoat seperti berikut ini.
Penutup
Benzena merupakan senyawa dengan enam atom C yang membentuk cincin dengan satu atom H di setiap atom C dan ikatan rangkap selang-seling.
Benzena memiliki berbagai turunan yang sering kita temui. Demikian pembahasan kita kali ini, semoga bermanfaat bagi kita semua







